How to Protect Online Video Courses: Anti-Hotlinking, Watermarks, DRM Encryption, and Copyright Strategies
Under the sweeping wave of digitalization, online video courses have become an important bridge for the dissemination of knowledge. Digital courses, as the crystallization of educators' wisdom and painstaking efforts, contain unique value in every frame and every line of explanation. However, the shadow of copyright infringement always looms large. For online video course websites to protect videos, the following aspects can be taken into consideration:
Anti-Leeching to Prevent Video Downloads

- Principle: Anti-leeching works by setting access rules on the server to validate the request source. When a user requests video resources through a browser or other client, the server checks the request's Referer header to verify if it originates from an authorized domain or path. If the source does not comply with predefined rules, such as coming from an unknown third-party URL or an unauthorized link, the server denies access to the video data. Additionally, a token-based mechanism can be employed, generating a unique token for each legitimate playback request. Only requests carrying a valid token can access the video, thus preventing unauthorized downloads.
- Advantages: Effectively blocks simple illegal download attempts, reducing the risk of video content being widely distributed. It prevents unauthorized websites from directly referencing and downloading the videos, protecting the content's copyright without affecting the viewing experience of regular users.
- Disadvantages: Advanced users may bypass the anti-leeching mechanism by modifying the Referer header or obtaining tokens through technical means. This method does not entirely eliminate the possibility of video theft. Furthermore, overly complex verification mechanisms may burden the server, impacting playback smoothness.
Video Watermark Displaying User Information
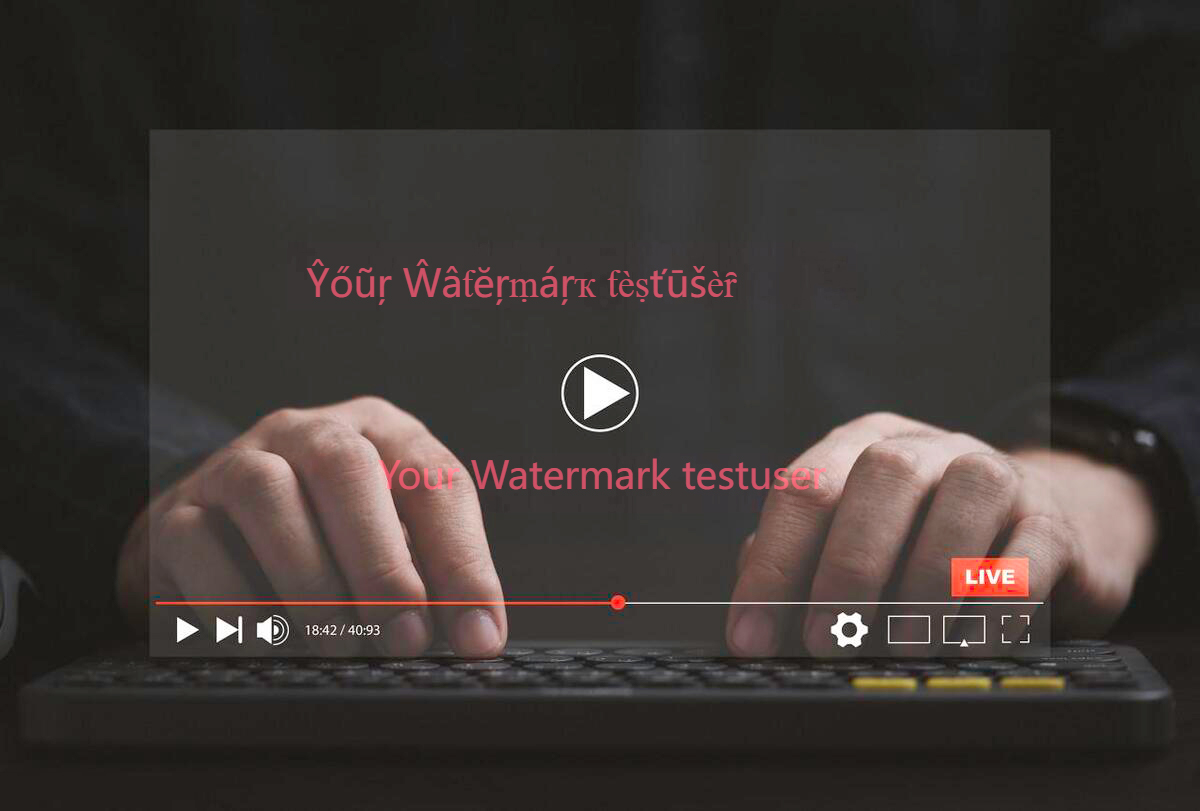
- Principle: Watermarks are added to the video interface using JavaScript (JS). When users log in and play videos, the system dynamically retrieves their key information, such as username or user ID, via JS code. This information is then displayed as text or semi-transparent overlays at specific positions on the video playback area. The watermark remains visible throughout the playback, marking the user's identity.
- Advantages: Easy to implement with simple JS code. By dynamically linking user information to the watermark, it deters potential pirates since videos with identifiable watermarks make the source of piracy traceable. This significantly increases the cost of piracy.
- Disadvantages: Skilled users may remove watermarks using video editing software or specialized tools. Improper watermark design—too opaque, too transparent, or poorly positioned—may affect the viewing experience or make it easy to crop or erase. Additionally, screen recording can still capture the original video, rendering the watermark ineffective against such actions.
Encrypting Videos with DRM Technology

Reference: "A Comparative Study of DRM-X, Widevine DRM, and VdoCipher Digital Rights Management (DRM) Technologies"
- Principle: Digital Rights Management (DRM) technologies, such as Google’s Widevine DRM or Haihaisoft's DRM-X, encrypt video content at the source. Taking DRM-X as an example, private encryption algorithms encrypt video files, producing protected content. During playback, the player interacts with the DRM server, sending a playback request along with device-related information. The DRM server verifies the device's authorization and sends a decryption key certificate to authorized devices. The player uses this certificate to decrypt and play the video. Throughout this process, encryption keys and licenses are strictly managed on the server, ensuring only authorized devices and users can access the content.
- Advantages: Provides robust content protection; even if the video files are stolen, they cannot be played without the proper decryption key. Technologies like DRM-X support multiple playback modes, including online streaming and local download playback, enhancing usability. DRM-X also offers screen recording protection, hardware binding (one device per license), and integrated watermarking, significantly enhancing security. These features are essential for protecting online course copyrights and securing creators’ interests.
- Disadvantages: DRM systems can be complex and may face compatibility issues, particularly on older devices or uncommon players. Continuous updates are necessary to maintain compatibility. Widevine DRM, for instance, is limited to online playback and cannot prevent browser-based screen recording, which reduces security in certain scenarios.
Copyright Registration for Legal Protection

- Overview: Copyright registration involves applying for intellectual property rights for online courses through relevant copyright offices. This process establishes legal protection for the course as original content. Applicants need to prepare detailed materials (course details, author information, work samples, and creative descriptions) and submit them online or offline. Upon approval, a copyright certificate is issued, providing legal safeguards for creators’ rights. In cases of infringement, the copyright holder can use the certificate to demand cessation of infringement and compensation through legal channels.
- Advantages: Legal Authority: The copyright certificate serves as the strongest evidence in legal disputes, effectively protecting creators’ rights and supporting legal action against infringement.
- Deterrence: The presence of a copyright itself acts as a significant deterrent, discouraging potential infringers from illegally using the content.
-
Disadvantages:
- Complex Application Process: Preparing detailed materials and ensuring their accuracy can be time-consuming and labor-intensive.
- Lengthy Review Cycle: The application process may take considerable time for approval.
- Cost: Application fees, material preparation costs, or professional consultation fees can be burdensome, especially for small creators or projects with limited budgets.
Conclusion
The choice of video protection strategy should depend on the security requirements of the website or creator, as well as the available resources.
For lower-security requirements: Anti-leeching and video watermarking are cost-effective and straightforward solutions.
For high-security requirements: Video encryption using DRM technology is essential, especially for creators dealing with commercial or high-value content. DRM encryption ensures robust protection against unauthorized access and playback.
For comprehensive protection: Copyright registration provides a strong legal foundation, offering creators the ability to legally address infringement and deter potential violators.
By carefully selecting and combining these strategies, content creators can effectively safeguard their video assets and copyrights.

